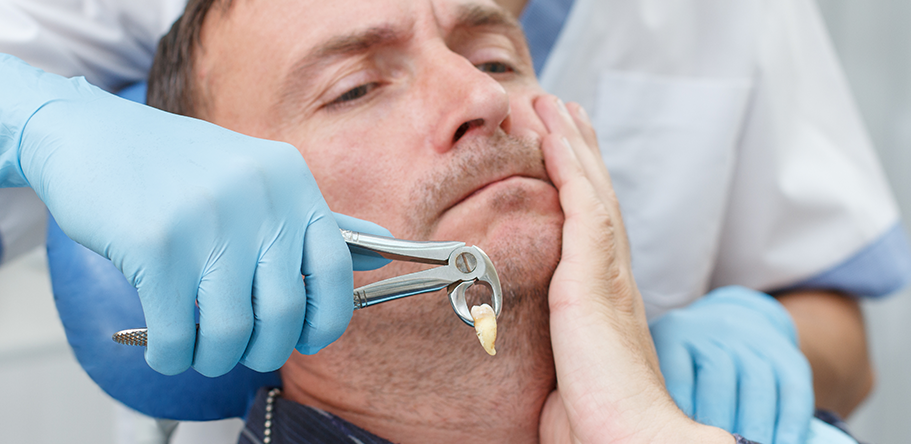
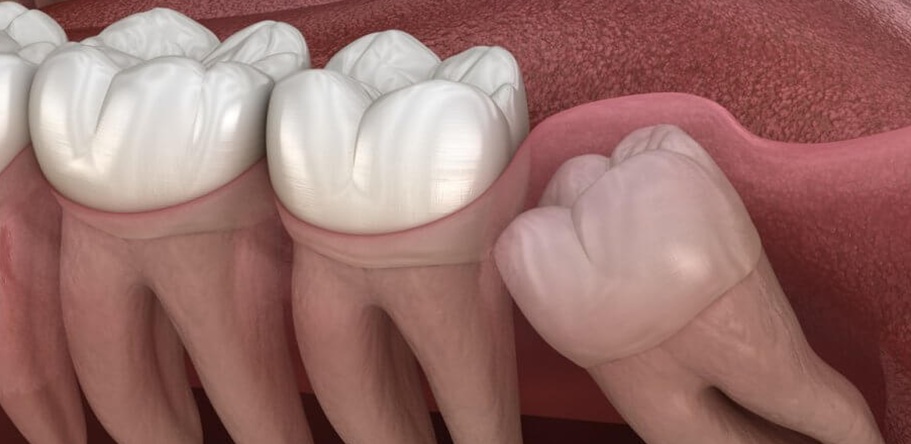
Surgical Extraction
Dental Surgery
Surgical Extraction
Procedure to remove teeth that cannot be removed easily
A surgical dental extraction is a procedure in which a tooth is removed that cannot be taken out through a simple extraction. This may be necessary in cases of impacted teeth (such as wisdom teeth), teeth that are broken or fractured below the gum line, or situations where infections or diseases affect the structure of the tooth or jaw, even teeth with horseshoe-shaped roots or close to nerves. During this procedure, the dentist or oral surgeon makes an incision in the gum to access the tooth and may use specialized tools to separate it from the surrounding tissues before removing it. This type of extraction typically requires local or general anesthesia and may involve a longer recovery time compared to simple extractions.
Surgical Extraction
Benefits
Pain relief
Extracting a problematic tooth, such as an impacted or infected tooth, can relieve intense pain and discomfort, improving the patient's quality of life.
Prevention of complications
Removing problematic teeth helps prevent future complications, such as recurrent infections, damage to adjacent teeth, or jaw problems.
Dental alignment problems
Not removing the tooth may cause crowding or malocclusions, complicating future dental treatments and affecting chewing function.
When to visit thedentist?
Visit the dentist every 6 months for a dental check-up.
Impacted teeth
Fractured teeth
Severe periodontal disease
Cysts or tumors
Irreparable teeth
Preparation for orthodontics
Surgical Extraction
Consequences
to undergo extraction may lead to prolonged pain and discomfort, affecting the patient's quality of life and daily activities.
Misaligned teeth are more difficult to clean properly, increasing the risk of cavities and periodontal diseases in the long term.
Having misaligned teeth can affect a person's confidence and self-esteem, influencing their social and professional interactions.
What does the service include?
Painless process: Local anesthesia is used. In most cases, a CBCT (special X-ray) is required to assess the position and depth of the wisdom tooth roots, ensuring patient safety and treatment success.
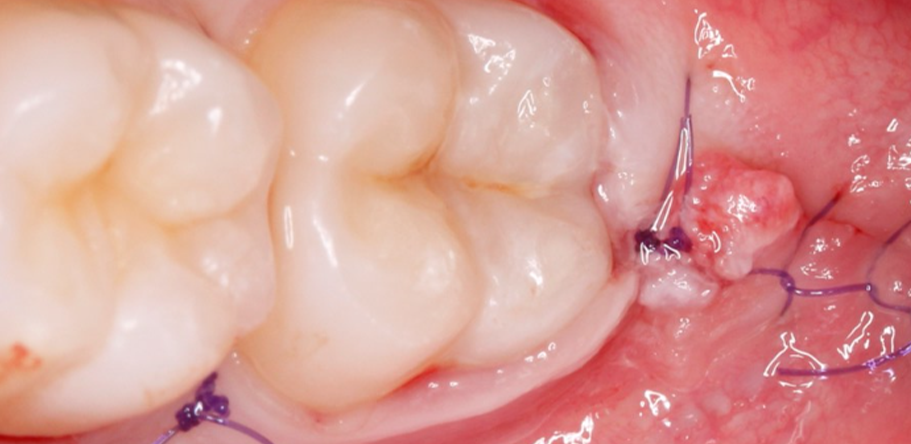 Después
Después
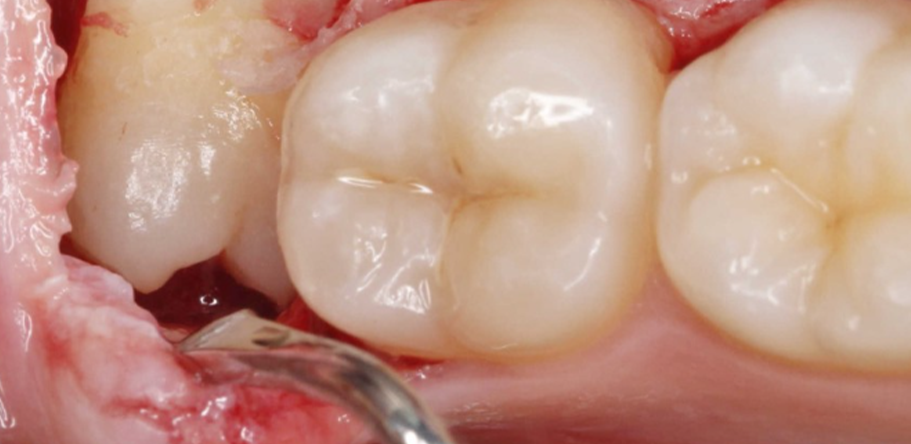 Antes
Antes
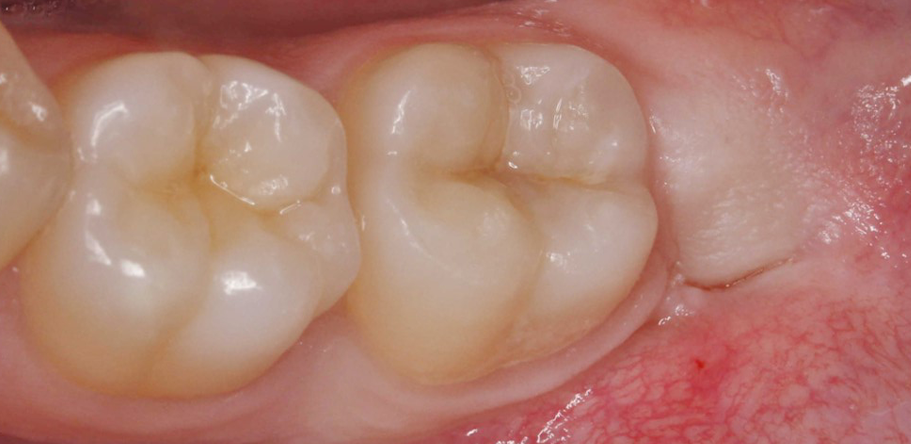 Después
Después
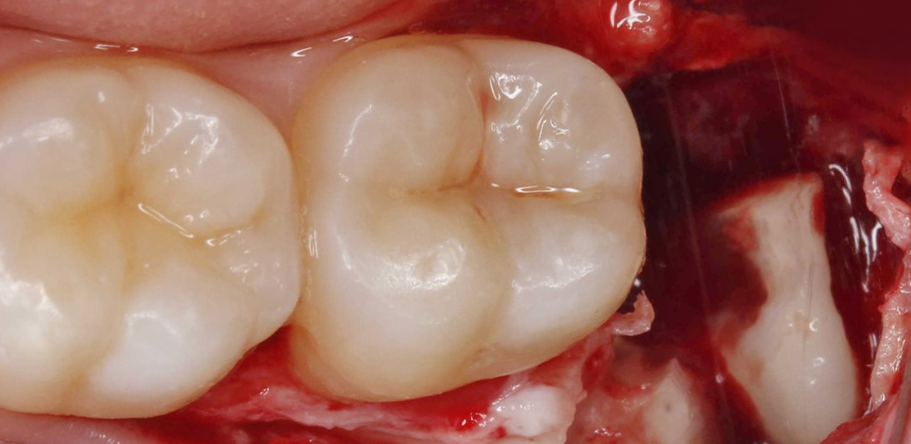 Antes
Antes